Remote Request
In the form designer, dynamically modify request parameters before initiating remote requests, such as adding authentication tokens or user IDs. Use the beforeFetch event and variables.
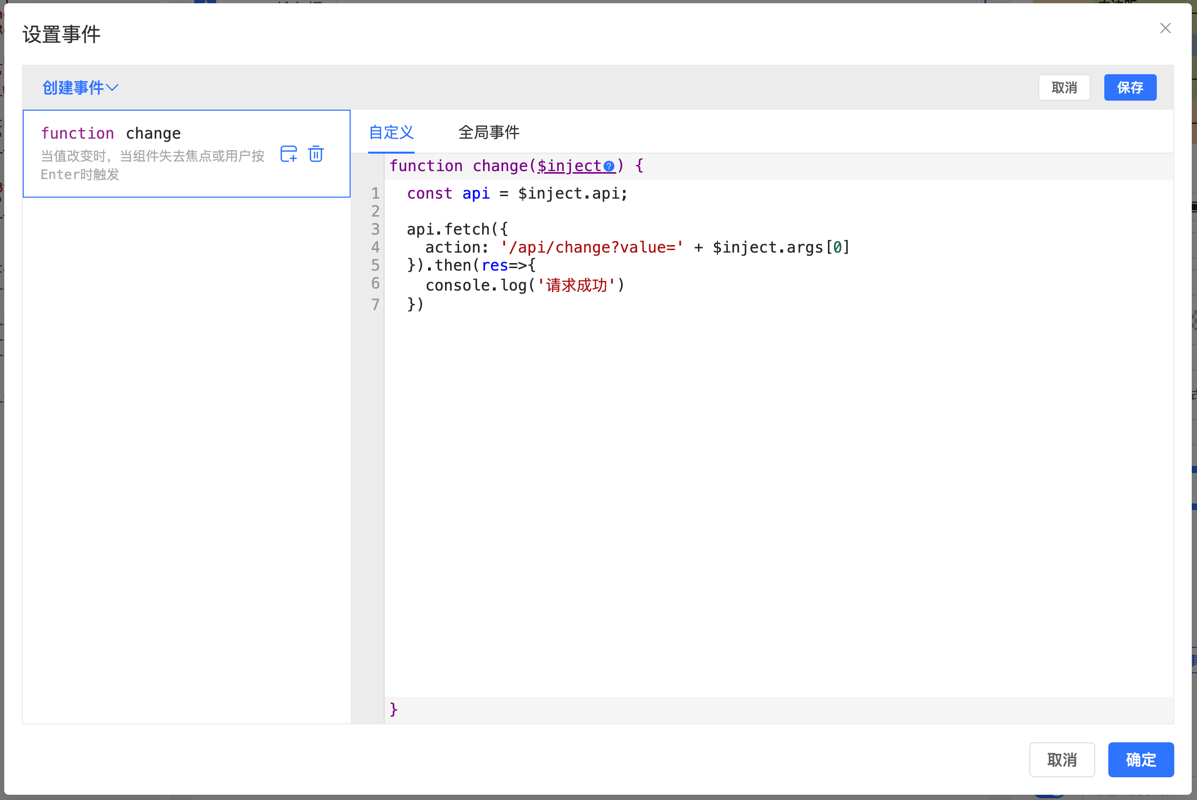
Data Structure
type FetchConfig = {
// Request URL
action: String;
// Request method
method?: 'GET' | 'POST';
// GET parameters
query?: Object;
// Data carried when sending request
data?: Object;
// Data sending method
dataType?: 'json' | 'formData';
// Request headers
headers?: Object;
// Post-request data callback
parse?: Function;
// Callback after successful request
onSuccess: (body: any) => void
// Callback after failed request
onError?: (e: Error | ProgressEvent) => void;
}Note
To set the request body to JSON format, define dataType as 'json'.
Send GET Request
Send a GET request to get configuration data for the corresponding Select component through the name parameter:
const formData = api.formData();
api.fetch({
action: '/api/getdata',
query: {
name: formData.name
}
}).then(res=>{
api.getRule('select').props.options = res.data;
});Send POST Request
Send a POST request to submit form data:
const formData = api.formData();
// External variable
const token = api.getData('globalToken');
api.fetch({
action: '/api/submit',
method: 'POST',
dataType: 'json'
data: formData,
headers: {
token: token
}
}).then(res=>{
// Form submission successful
});Using Variables in Requests
When configuring requests, use double curly braces {{ }} to reference variables. Variables are supported in URLs, request headers, and data. For example, {{token}} is replaced with the token variable value when the request is made. If the variable value is an object, access property values through {{variableName.attributeName}}.
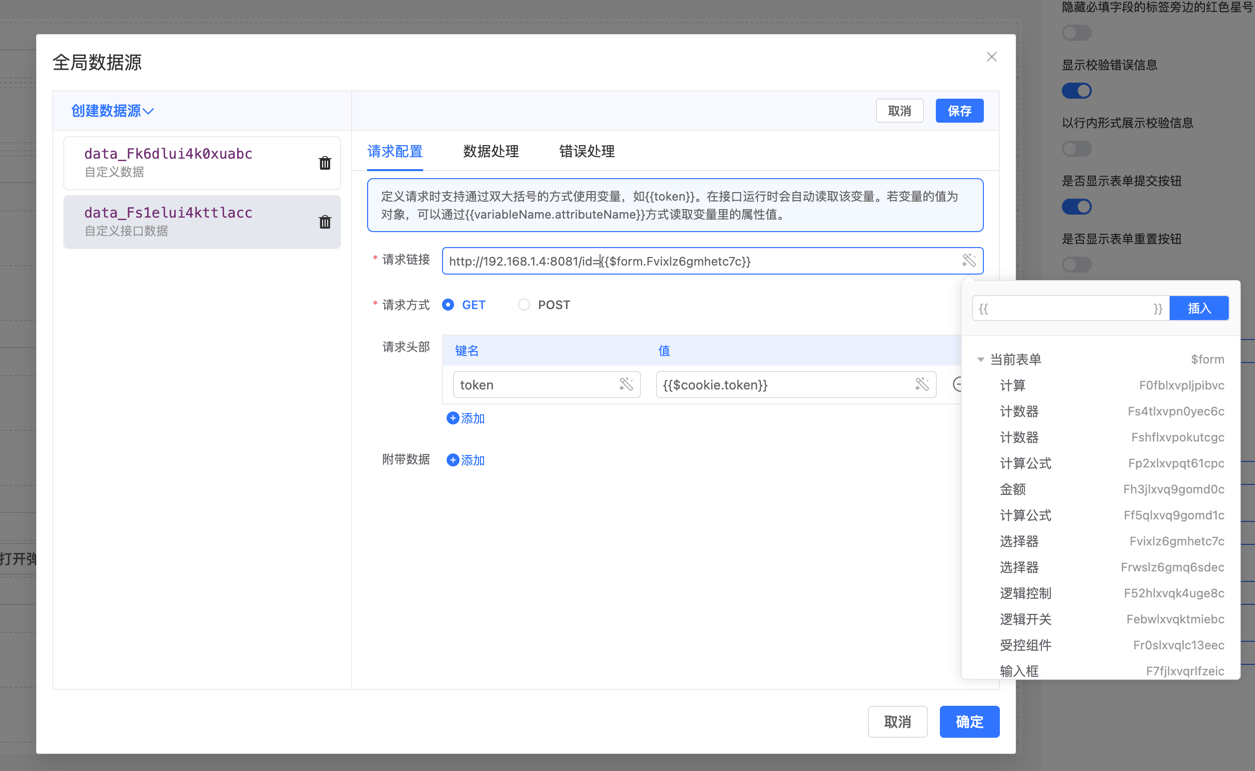
Example
Suppose we have a remote API request that needs to dynamically insert a user's Token and ID. Use the double curly braces {{ }} syntax in the configuration:
Request URL Example (GET Method)
To insert dynamic variables in your request URL, such as user ID, use the double curly braces syntax:
api.fetch({
action: 'https://api.example.com/user/{{$form.userId}}/details',
method: 'GET',
headers: {
'Authorization': 'Bearer {{$cookie.token}}'
},
data: {},
}).then(res=>{
//todo
});When the actual request is executed, {{userId}} and {{token}} are replaced with actual variable values.
Request Data Example (POST Method)
The data portion of the request can also use variables for dynamic settings:
api.fetch({
action: 'https://api.example.com/update',
method: 'POST',
dataType: 'json',
headers: {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'Authorization': 'Bearer {{$cookie.token}}'
},
data: {
name: '{{$form.userName}}',
age: '{{$form.userAge}}'
},
}).then(res=>{
//todo
});Variable Replacement in Requests
During the actual request process, the designer automatically replaces variable values in double curly braces. For example:
{{$cookie.token}}is replaced with the token field in cookie{{$form.userId}}is replaced with the userId field in the form{{$form.userName}}is replaced with the userName field in the form{{$form.userAge}}is replaced with the userAge field in the form
Supports using {{variableName}} to directly read built-in variables, global variables, and externally passed data. For specific definition methods, see the Variable Usage Documentation
Modify Requests Through Pre-event
The beforeFetch event is a callback function triggered before sending a request. Modify request parameters in this callback, such as adding request headers, modifying request URLs, adding query parameters, etc.
Note
The data obtained in the beforeFetch event is the final request data, and template variable parsing is no longer supported.
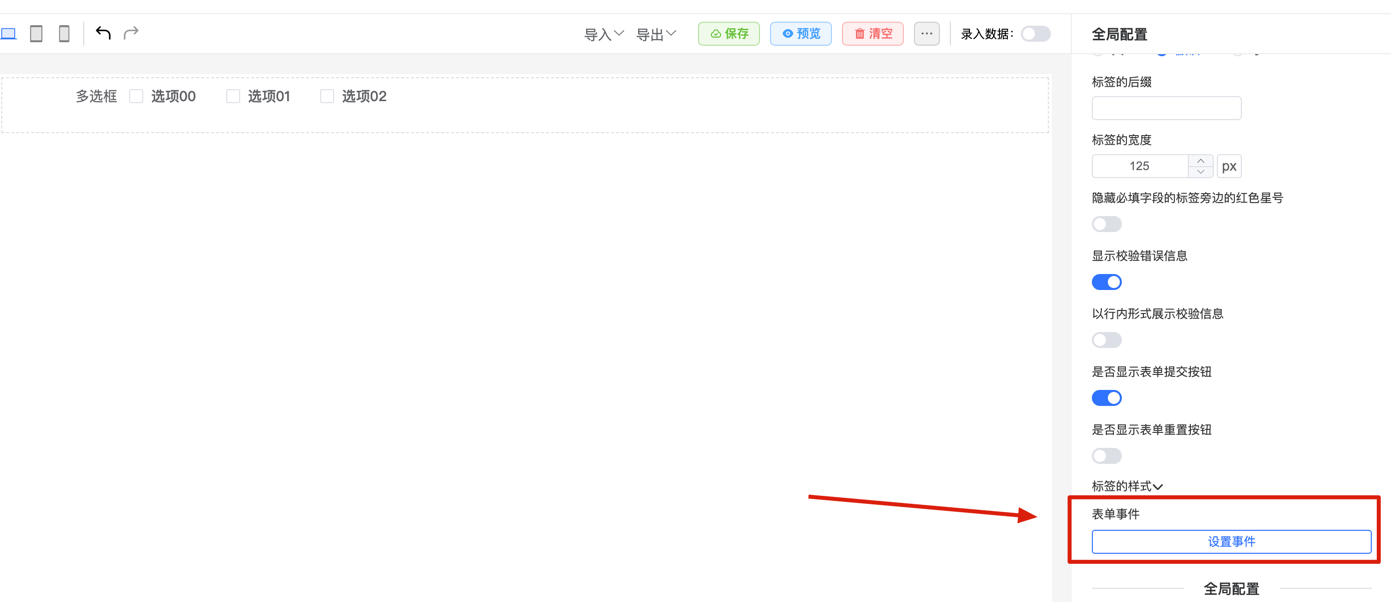
1. Open Form Event Configuration Dialog
Enter the form designer and click the "Events" option in the configuration panel to open the event configuration dialog.
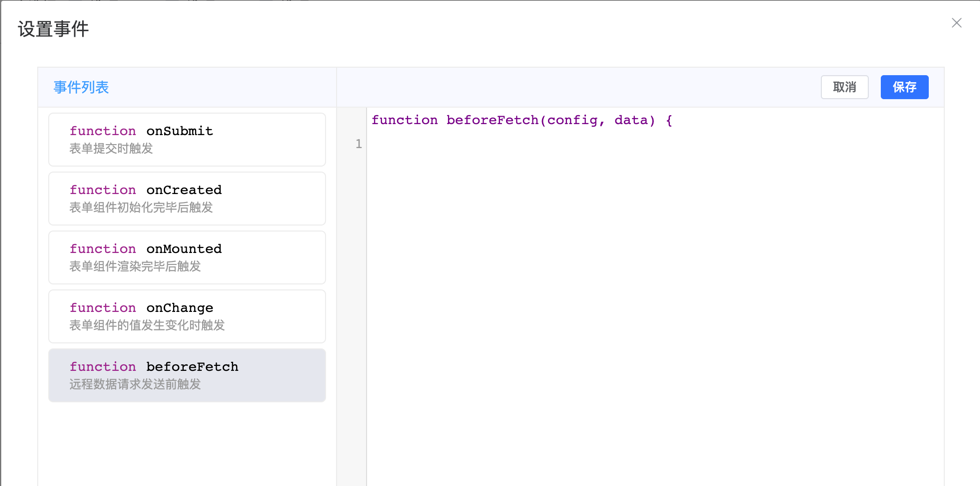
2. Configure beforeFetch Event
In the event configuration dialog, select the beforeFetch event and enter:
3. Modify Parameters
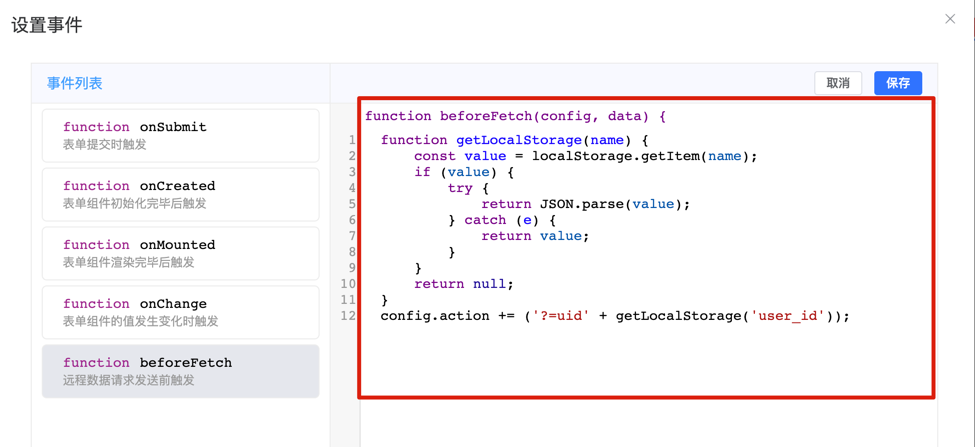
For example, add token to request headers:
function getCookie(name) {
name = name + '=';
const decodedCookie = decodeURIComponent(document.cookie);
const cookieArray = decodedCookie.split(';');
for (let i = 0; i < cookieArray.length; i++) {
let cookie = cookieArray[i];
while (cookie.charAt(0) === ' ') {
cookie = cookie.substring(1);
}
if (cookie.indexOf(name) === 0) {
cookie = cookie.substring(name.length, cookie.length);
try {
return JSON.parse(cookie);
} catch (e) {
return cookie;
}
}
}
return null;
}
config.headers.token = getCookie('user-token');For example, add user ID to request URL:
function getLocalStorage(name) {
const value = localStorage.getItem(name);
if (value) {
try {
return JSON.parse(value);
} catch (e) {
return value;
}
}
return null;
}
config.action += ('?=uid' + getLocalStorage('user_id'));For example, add custom token variable to headers:
config.headers.token += data.api.getData('token');Post-request Callback
parse is a post-request callback function used to process returned data after the request is completed. Format, convert, or perform other processing operations on the data in the parse function for use in components.
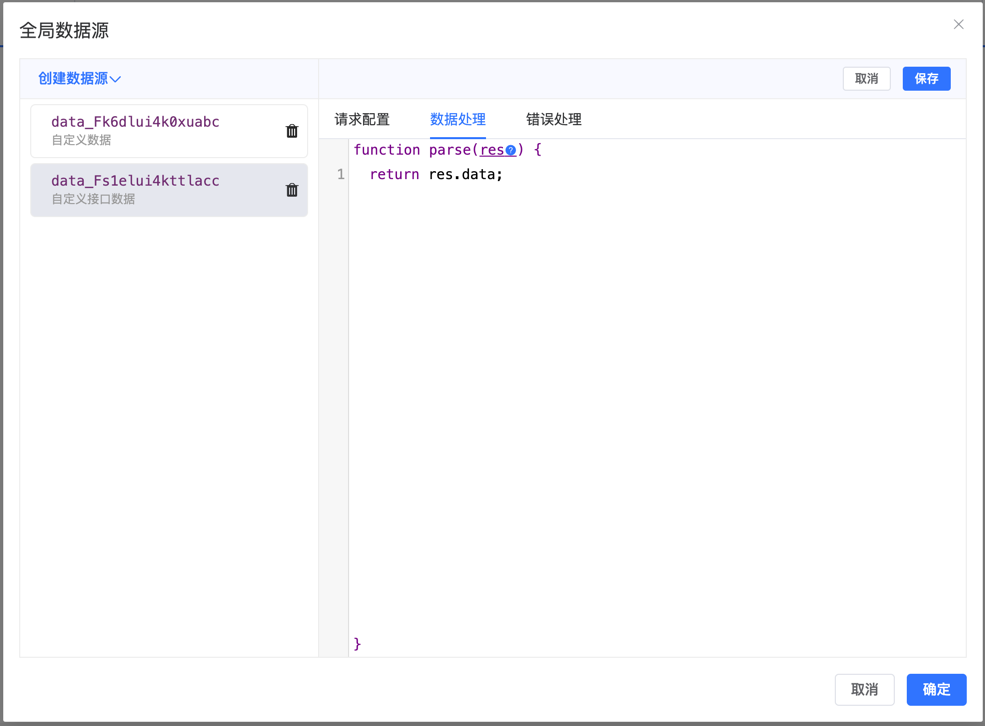
Example: Parse and Process Request Results
Suppose you have an API interface that returns data in the following format:
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"items": [
{ "id": 1, "name": "Item 1" },
{ "id": 2, "name": "Item 2" }
],
"total": 2
}
}Use the parse function to process this data. For example, extract data.items and format it into another structure.
Example Code
Use the parse function to process data returned from an API request and format it into an array containing item names:
function parse (data) {
if (data.status === 'success') {
// Extract and format data
return data.data.items.map(item => ({
id: item.id,
name: item.name
}));
} else {
throw new Error('Request failed');
}
}
</script>Send Requests Through API
Manually send remote requests through the api.fetch method in events:
api.fetch({
action: '/api/getdata',
query: {
name: api.getValue('name')
}
}).then(res=>{
//todo
});Override Built-in Request Method
Modify the built-in request sending method by overriding formCreate's fetch method, thereby dynamically modifying request parameters:
Note
File upload operations also call the fetch method. Pay attention to its special adaptation requirements. For specific implementation, see the Built-in Request Module.
import FcDesigner from '@form-create/designer'
const globalFetch = FcDesigner.designerForm.fetch;
FcDesigner.designerForm.fetch = FcDesigner.formCreate.fetch = (config) => {
config.headers.token = getCookie('user-token');
return globalFetch(config);
}

